Android App Manifest The Android App Manifest contains information about an Android application. Each application has a single Android App Manifest XML file at the root of the source set called AndroidManifest.xml. So, any not-so-simple text editor is sufficient to create four empty files named AndroidManifest.xml, Info.plist, config.xml, and, guess what, another config.xml. What's next is to copy and paste the following templates (already available in Graphite and Mist) and save the changes. AndroidManifest.xml 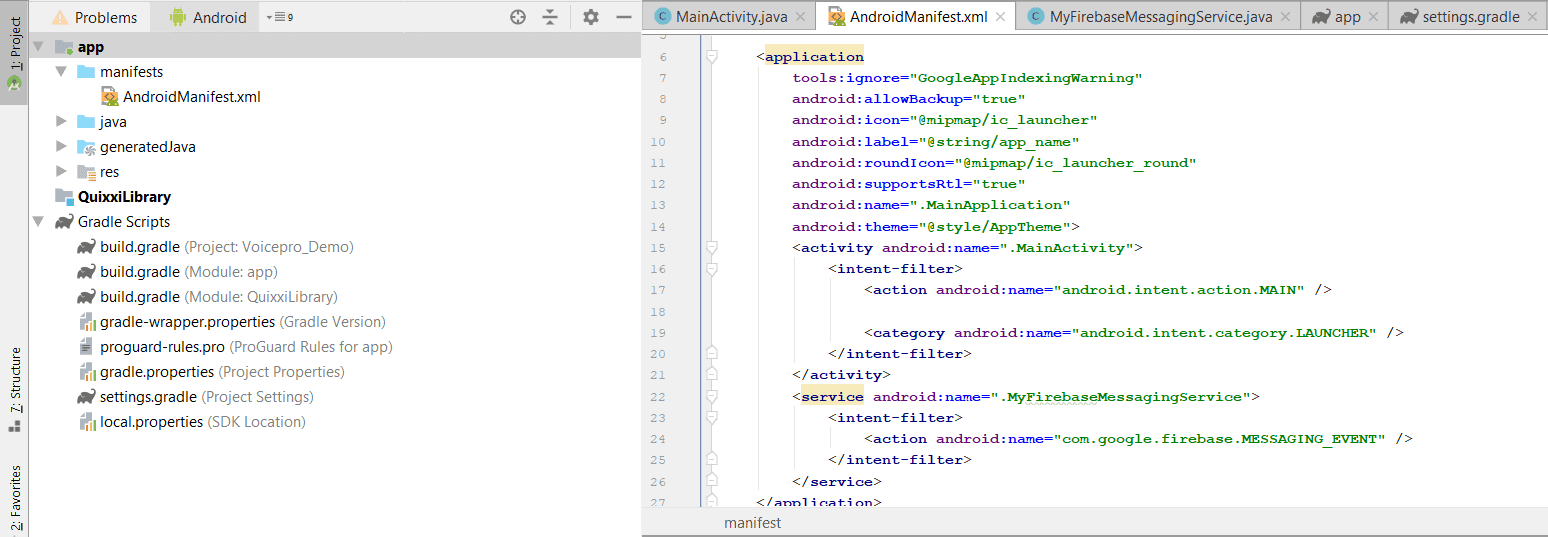
Android Quixxi Security
The new manifest editor solves the above issue. It allows developers to add or modify elements in the manifest while also allowing the compiler to add the standard elements. Choosing Project - Manifest Editor will open the editor: As shown in the above screenshot the editor starts with several default elements. Image Editor with an automatic format cross-conversion to replace Android images. Code Editor with a syntax highlighting for XML, YAML, and Smali. Android Explorer to manage files on your Android device and take screenshots. Permission Editor to easily add or remove Android permissions. Manifest Editor including a handy API level selector.
Open the AndroidManifest.xml file with a text editor. This is the file that holds information about the app, such as the version and permissions. Edit the existing tags in the file or add new ones as needed. Save your changes. Use the APK Tool to compile the modified .apk file. Test your modified .apk file on an Android device or emulator. O Android Manifest Editor. This presents the Android Manifest Overview screen, as shown in Figure 3-1. This screen gives you a high-level view of your application structure, enabling you to set your application version information and root level manifest nodes, including withAndroidManifest plugin function require the current configuration as the first param and a callback which is the editor. modResults.manifest is the object representing the android androidManifest file, by returning the modified object we will get a manifest file similar to the following (we can check this with expo prebuild) Oct 26, 2022, 4:27 AM I have created a new Android project in VS for Mac 2022 but I cannot find the Android Manifest Editor to open the AndroidManifest.xml file. In VS for Mac 2019, I used the Android Manifest Editor to open and edit the file. But VS for Mac 2022 only displays the source code version of AndroidManifest. The manifest file describes essential information about your app to the Android build tools, the Android operating system, and Google Play. Among many other things, the manifest file is required to declare the following: The components of the app, including all activities, services, broadcast receivers, and content providers. Android Studio is the official Integrated Development Environment (IDE) for Android app development. Based on the powerful code editor and developer tools from IntelliJ IDEA , Android Studio offers even more features that enhance your productivity when building Android apps, such as: A flexible Gradle-based build system. AndroidManifest.xml is one of the most important files in your entire project, providing essential information to the Android build tools, the Android operating system and the Google Play. How to get GUI to edit androidmanifest.xml in Android Studio? Ask Question Asked 7 years, 5 months ago Modified 6 years, 10 months ago Viewed 6k times 5 I am new to Android technology. I installed Android Studio and want to add Application attributes in the androidmanifest.xml for the sake of Shared Preferences. Step1: Extract the AndroidManifest.xml file from apk using the apktool. Step2: Modify this extracted manifest file. You can modify other resources like icons, string resources as well in this step. Step3: Now we need to convert these modified resources into protobuf format. Please follow the below link for the same. Your APK or Android App Bundle file can contain just one AndroidManifest.xml file, but your Android Studio project may contain several manifest files provided by the main source set, build variants, and imported libraries. When building your app, the Gradle build merges all manifest files into a single manifest file that's packaged into your app. Your app name can be changed from strings.xml file in the res/values/ folder. You can do any formatting from within Eclipse itself during the development of your project/app. Look at the bottom of the Eclipse Editor Screen , you will see tabs, from that Tab, select last one "AndroidManiFest.xml" It will display Xml in Text Format. AndroidManifest.xml is generated as part of the build process, and the XML found within Properties/AndroidManifest.xml is merged with XML that is generated from custom attributes. The resulting merged AndroidManifest.xml resides in the obj subdirectory; for example, it resides at obj/Debug/android/AndroidManifest.xml for Debug builds. 
android Getting a manifest element not declared error Stack Overflow
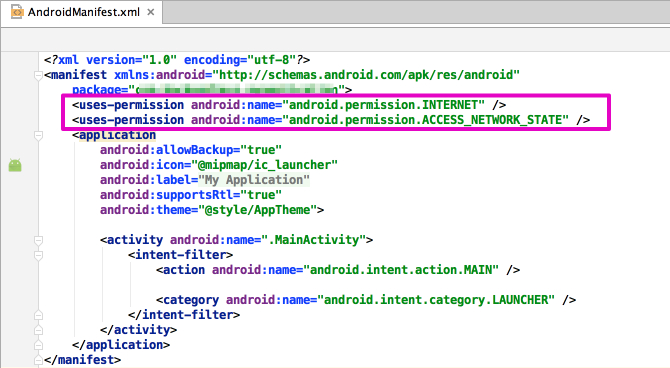
Quick Start Guide for Android Backend as a Service Platform

Android Lecture









